Nearly half (48.5%) of traffic to websites comes from bots, not human beings, according to a recent report from Imperva Incapsula.
The report was based on data from more than 19 billion visits to 35,000 Incapsula client websites around the world with a minimum daily traffic count of at least 10 human visitors. The data was collected over a 90-day period (July 24, 2015 - October 21, 2015) and was compared with findings from previous studies conducted by Imperva.
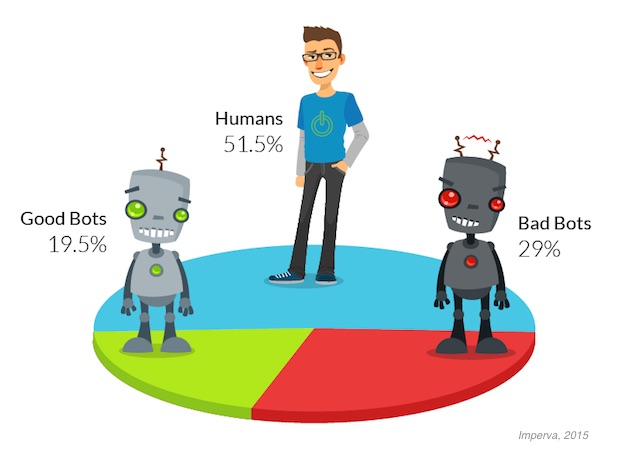
Some 51.5% of all the Web traffic examined came from humans, 29% came from "bad bots" (those used to automate spam campaigns, spy on competitors, launch denial of service attacks, execute vulnerability scans, etc.) and 19.5% came from "good bots" (those used by search engines, marketing research tools, SEO optimizers, uptime monitors, etc.).
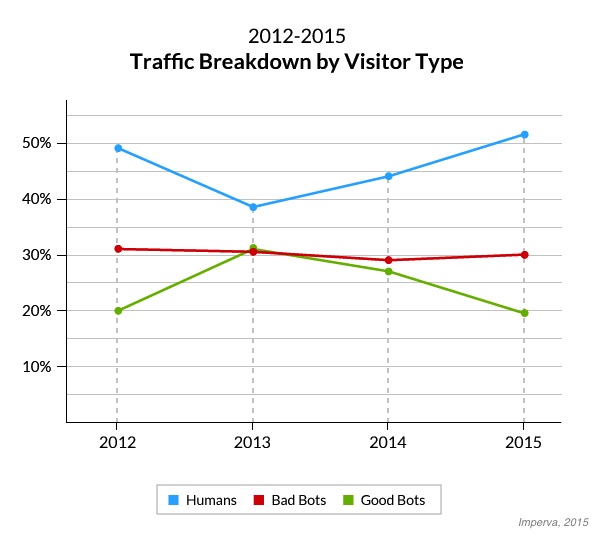
Overall, the share of human traffic to websites has risen over time, according to the report.
In a similar 2013 study conducted by Imperva, humans made up only 31.5% of all visits to sites, compared with 51.5% in 2015. This shift is mainly due to an increase in human traffic as more people use the Web and a decrease in good bot traffic.
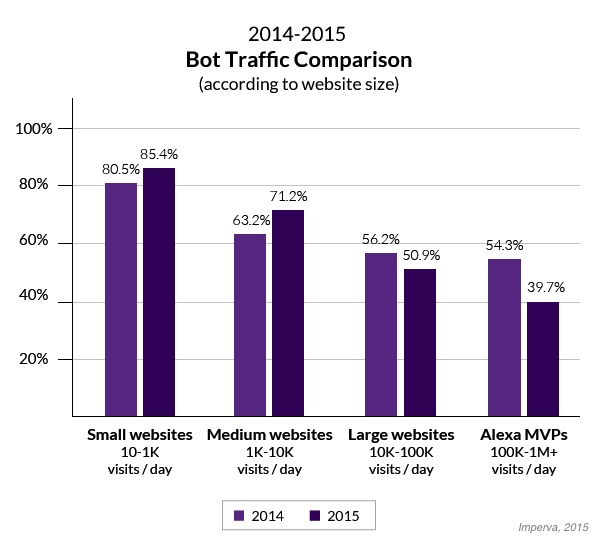
The ratio of bot-to-human traffic varies significantly based on website popularity, the analysis found.
The most popular sites examined, those with 100,000+ visits/day, have the smallest share of bot traffic (39.7%). In contrast, the least popular sites examined have the highest share of bot traffic (85.4%).
About the research: The report was based on data from more than 19 billion visits to 35,000 Incapsula client websites around the world with a minimum daily traffic count of at least 10 human visitors.




