Personal social networks and professional ones satisfy different needs and interests, and have different sets of emotional drivers that fuel them: People not only make different types of connections but also experience different sets of emotions, depending on network type, according to a study conducted by TNS for LinkedIn.
When visiting personal networking sites (e.g., Facebook, Twitter, and Pinterest) people experience emotions around memories and entertainment, whereas when visiting professional networks (e.g., LinkedIn, BranchOut, and BeKnown) people are motivated by the sense of purpose to achieve the goals they've set, the study found.
According to the top five drivers identified by the study, when using personal networks, people spend time being entertained, whereas when using professional networks, people invest their time to connect with people and brands that align with their drive for achievement and success:
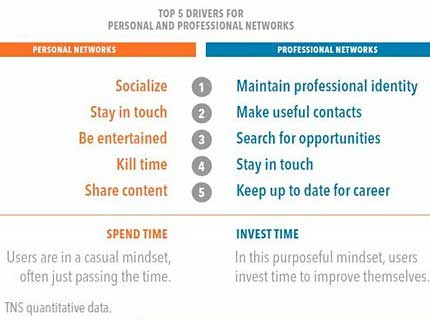
Below, additional findings from the study titled "Market to Mindset," which explores what motivates people when they visit social networking sites, and what type of content they prefer when they visit those sites.
Types of Content
The casual and purposeful mindsets create differences in the content people expect to see on each type of network.
Among professional social networkers, career information tops the list for preferred content, followed by updates on brands, and current affairs:

Types of Brand Content
The types of brand content that users want to see further reflect the mindset divide between spending time and investing time.
Among professional social networkers, content related to improving oneself professionally is most preferred (15%), followed by content that helps people make business decisions (10%).
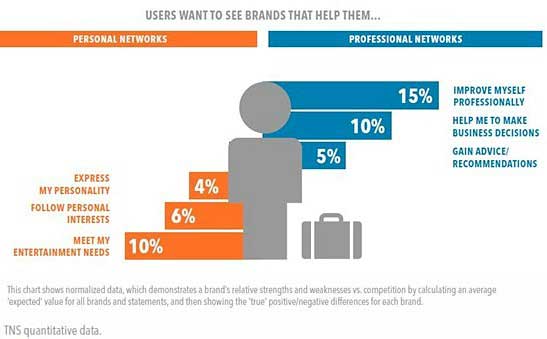
By contrast, among personal social networkers, content that entertains is most favorable (10%).
Types of Influence
The casual and purposeful mindsets are also reflected in users' motivations to connect and their ability to influence.
When using personal, social networks, 61% of people view influence in terms of sharing information with others, whereas 39% view influence as being the first to know.
On professional social networks, 65% view influence in terms of sharing information (7% more than for personal networks), whereas 45% view influence as being the first to know (15% higher than for personal networks).
About the data: This research was conducted by TNS on behalf of LinkedIn among more than 6,000 social media users (age 18+) across 12 countries, February to April 2012. The study was conducted in two stages consisting of quantitative and qualitative phases. Professional and personal networks were grouped by how users identified the majority of their connections. For the study, professional networks consisted of LinkedIn, BranchOut, BeKnown, Viadeo, and Xing; personal networks were Facebook, Twitter, Pinterest, and Orkut.




