Increases in worldwide spam volumes have driven ISPs (Internet service providers) to impose tougher filtering standards on email deliverability, making it harder for email marketers to maintain high sender reputations and deliverability levels, according to a study by Return Path.
A brand's sender reputation affects its ability to communicate with customers via email.
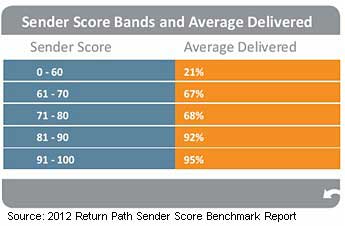
Using the Return Path Sender Score metric, which measures the ability of a business to deliver email to its customers, the study found that businesses with high sender reputations, or Sender Scores above 90, generate delivery rates of 95% on average. By contrast, businesses with lower sender reputations, Sender Scores between 60 and 89, record delivery rates of 68% on average. Most legitimate businesses fall into the latter category, Return Path found.
Below, additional findings from Return Path's latest study, The 2012 Sender Reputation Benchmark Report.
Spam in Perspective
"Spam" refers to email messages that get routed to spam filters, or blocked before they ever reach recipients' accounts. Most are sent from "illegitimate" and "unknown" accounts as well as millions of computers infested with Trojans and running as "zombies."
Such emails should never have been sent; no ISP should accept them. However, they account for over 85% of all emails exchanged, according to Return Path.
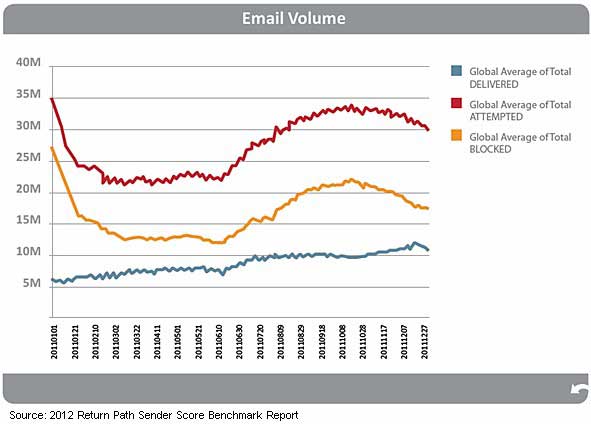
Spam levels fluctuate throughout the year, but they are on the rise overall, Return Path found.
After a significant drop in the beginning of 2011, spam volume steadily increased after July, as did the total number of messages blocked. Emails that were delivered (including emails filtered into spam folders) steadily increased throughout 2011:
Sender Score Composition
Sender Scores are calculated based on three key components:
- Complaints: The volume and percentage of emails from an IP address that recipients mark "spam."
- Unknown Users: The percentage of emails sent from an IP address to nonexistent addresses.
- Spam Traps: The number of emails sent from an IP address to decoy accounts that ISPs use to catch spammers.
Complaints Are a Big Factor
Complaints are registered when email recipients mark a message "spam," and they are the most important indicator affecting email deliverability, according to the report.
Total complaint volume spiked at two points in 2011. The first was from late February to early March. The second, more predictably, was in mid-November, as businesses ramped up email volume for the holiday season:
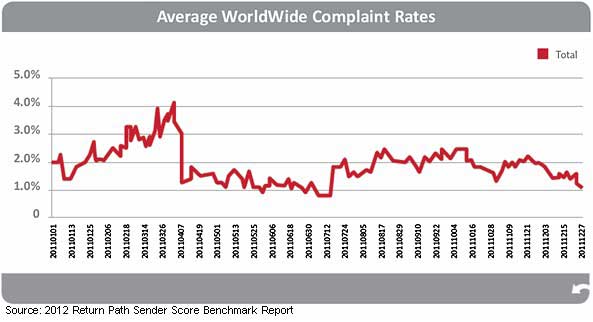
Email senders need to keep their complaint rates at one-tenth of one percent or below in order to avoid negatively impacting inbox placement, according to Return Path.
Key Deliverability Trends by Sector
Most industry sectors performed at or near global averages. However, there were significant outliers in a few categories:
- High frequency of spam traps were found among social networking senders. One of the most important tools social networks use to grow their subscriber base is the address books of their current users. However, this presents a risk: most email recipients do not actively manage their address books, resulting in numerous unused or abandoned email addresses being present. As a result, social networking sites were found to have an average of 20 spam traps.
- Social networking and gaming had the highest degree of unknown users. For reasons outlined above, social networking and gaming sites also have unusually high unknown user rates.
- The highest complaint rates occurred in social networking, banking, retail, and corporate services. Other industries had complaint rates above 2%, but social networking, banking, retail, and corporate services were the only sectors to approach or exceed 3% on average.
What Should Email Marketers Do?
Marketers can assess their own sender reputation against industry benchmarks using Return Path's tool (a mail server IP address is required).
In addition, marketers are advised to reduce complaint rates (via feedback loops, etc.) and practice good list hygiene. A full set of recommendations is included in the report.
About the data: Return Path conducted this study by monitoring data from its Reputation Network from January to December 2011. This study tracked the reputation rates for more than 130 million IP addresses sending nearly 20 trillion emails to ISPs in Return Path's Reputation Network. For each IP address, Return Path recorded total messages sent, delivered and blocked. Unknown users, complaints, and spam trap rates for each IP address were also reviewed to calculate Sender Scores.



