Though one-half (50%) of Americans read print or Web editions of newspapers for local information at least weekly, more than two-thirds (69%) say the death of their local newspaper would have no impact (39%) or only a minor impact (30%) on their ability to find local information, according to a report by Pew Research.
The Pew findings reflect a media landscape in flux, as well as Americans' growing appetite for multiple news sources: 64% of American adults surveyed say they get their weekly news from three types of media, with 15% reporting that they looked at up to six different media types.
Moreover, nearly one-half of Americans (45%) say they do not even have a favorite local news source.
Below, additional findings from the report titled, "How People Learn About Their Local Community," issued by the Pew Research Center's Internet & American Life Project and Project for Excellence in Journalism in partnership with John S and James L Knight Foundation.
Tapping a Variety of Media Outlets
Americans consume different kinds of media for different kinds of information. Among all surveyed adults:
- Television is the preferred medium for breaking news and weather, though TV ties with radio as the top source of traffic news.
- Newspapers are still the top source for 11 other topics studied by Pew such as local government updates, community events, arts and culture, social services, taxes, zoning news, and crime reports.
- The Internet is the top source of information on restaurants and other local businesses.
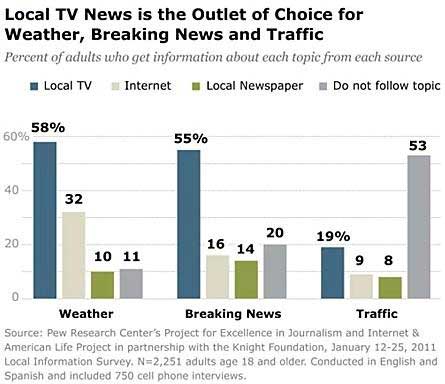
But even as the Web has gained traction, there is one area where it still lags behind: breaking news. Here, local TV news (which includes local TV websites but is driven almost entirely by broadcasts) still outpaces online sources.
Among all adults, 55% say they rely on local TV for breaking news, compared with 16% who say they rely on the Internet and 14% who rely on newspapers:
Top Local Information Source: TV
Among all American adults, TV is the top source of local news (74%), followed by second-ranked word of mouth (55%), radio (51%), newspapers (50%) and the Internet (47%).
Word-of-mouth sources are defined in the study as information from friends, family, co-workers, and neighbors. For at least some, the reliance on word of mouth is tied to the use of social networking sites, now used by 61% of Internet users, according to Pew.
The Internet category comprises search engines (41%), social networks such as Facebook (11%) or Twitter (3%), or websites (10%) or blogs (4%) devoted to the local community (and not associated with a traditional media source such as a TV station or newspaper.
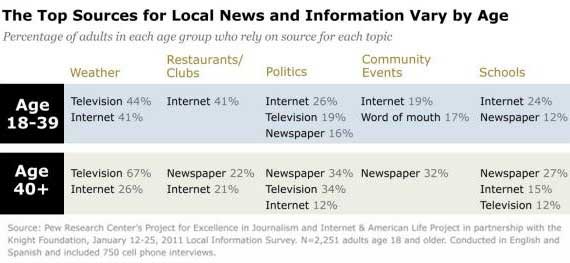
Age Matters
Reliance on media sources varies by age. Older consumers age 40 and over still rely more heavily on traditional platforms for topics such as weather, politics, and community events, whereas younger consumers rely more on the Internet for topics politics, community events, schools, and restaurants and clubs.
Where the Web Rules
Among all adults, the Internet is the top source of information for 5 out of the 16 local topics in the survey, including restaurants, local businesses, schools, housing, and local jobs—though it ties with newspapers in the last three areas.
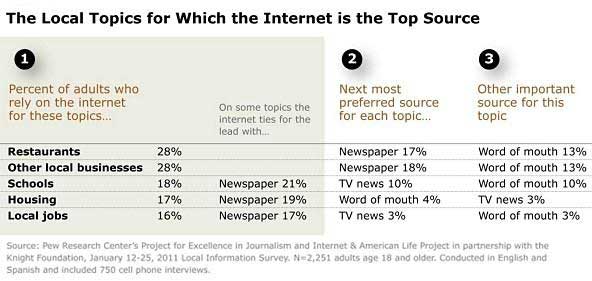
Beyond the topics for which it is the top source, the Internet is often the second-most important source of information on a variety of other topics such as community events, weather, and local arts and cultural activities.
Looking for great digital marketing data? MarketingProfs reviewed hundreds of research sources to create our most recent Digital Marketing Factbook (May 2010), a 296-page compilation of data and 254 charts, covering email marketing, social media, search engine marketing, e-commerce, and mobile marketing. Also check out The State of Social Media Marketing, a 240-page original research report from MarketingProfs.
Internet-Savvy: Mobile and Participatory News Consumers
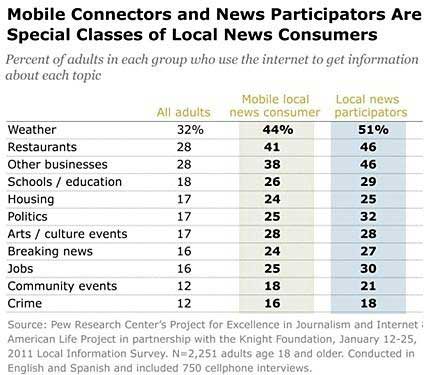
Nearly one-half (47%) of adults get at least some local news and information via their smartphones or tablet computers.
Although mobile does not top the list of preferred sources for any of the 16 topics examined, it is still a widely used supplemental source in areas such as checking weather reports (36%), finding local restaurants or businesses (31%), finding community news (25%), sports scores (20%), local traffic or transportation information (19%), and finding local coupons or discounts (16%).
In addition, 11% of adults say they get local news from apps for their smartphones.
On the participatory side, 41% of adults can be considered "local news participators," meaning they say "yes" to at least one of the following:
- Share links to local stories or videos online with others: 25%
- Commented on local news stories or blogs they read online: 16%
- Posted news or information about local community on a social networking site such as Facebook: 16%
- Contributed to online discussions or message boards about their community: 8%
- Have "tagged" or categorized online local news content: 6%
- Contributed articles, opinion pieces, photos, or videos about their local community online: 5%
- Posted news or information about their local community on Twitter: 2%
Those who are interested in finding local information via handheld device, or participates in circulating local information, are far more likely than others to rely on the Web for most of the 16 topics.
That is particularly true for participators, who are 1.6 times more likely than adults on average to use the Internet to find information on businesses (46% vs. 28%), restaurants (46% vs. 28%), and breaking news (27% vs. 16%):
About the survey: Findings are from Pew's report How People Learn About Their Local Community, authored by Tom Rosenstiel, Amy Mitchell, Kristen Purcell, and Lee Rainie, issued by the Pew Research Center's Internet & American Life Project and Project for Excellence in Journalism in Journalism in partnership with John S and James L Knight Foundation, September 26, 2011, accessed on October 5, 2011. Data are based on a survey of 2,251 adults, age 18 and older, conducted by Princeton Survey Research Associates International, January 12-25, 2011. Interviews were conducted via telephone in English and Spanish by landline (1,501) and cell (750).



