How do you strike the right balance between delivering personalized marketing experiences and protecting user privacy? Is it a zero-sum game in which one goal undermines the other, or can they harmoniously coexist?
This article will explore practical approaches and best-practices for reconciling those seemingly conflicting goals.
We'll delve into the intersection of privacy and personalization, highlighting how businesses can foster trust, comply with ever-evolving data regulations, and still deliver the individualized experiences that customers value deeply.
The ultimate aim? To place user-centric privacy at the core of marketing practices, creating a symbiosis that drives both customer satisfaction and business success.
Building Trust: Privacy and Personalization Intersection
Building trust in the digital sphere necessitates a three-pronged approach:
- Maintain an open dialogue with customers by providing clear and accessible privacy policies, and by promptly answering any data usage inquiries.
- Communicate the value that customers receive from sharing their data, such as improved services or personalized experiences; that approach should encourage them to share their data.
- Respect customer data preferences, giving them the flexibility to choose how much data they share.
Implementing a user-centric privacy approach calls for a series of practical steps that intertwine data privacy and marketing requirements:
- Use data anonymization to maintain privacy while gaining valuable insights: Data masking, pseudonymization, and generalization protect sensitive information.
- Machine-learning algorithms analyze large volumes of data to uncover actionable insights. Select a suitable tool—for example, TensorFlow, Keras, or PyTorch—and apply relevant machine-learning models to meet your objectives.
- Avoid indiscriminate data collection that risks privacy and incurs unnecessary overheads. Instead, identify key data; explain to customers why it's necessary and how it enhances their experience.
- Take a cue from Apple's App Tracking Transparency feature: Be clear about what data you're collecting, why, and how it will be used. Request consent before tracking data, keeping the process simple and user-friendly.
The Art of Consent-Based Marketing
Consent-based marketing—requiring clear and informed consent for data collection and use—is quickly becoming the norm.
The principles of consent-based marketing are clarity, voluntariness, and specificity:
- When asking for consent, jargon and convoluted language have no place. Users should know exactly what they're consenting to.
- Consent should also be given freely, and users should never feel pressured into it.
- Consent requests should be specific to different processing activities and separated from other terms and conditions.
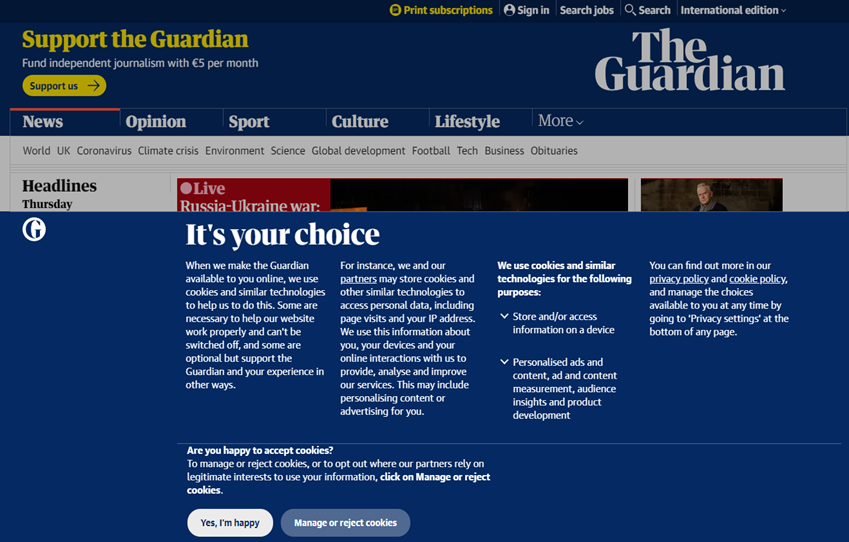
Here, for example, is the Guardian newspaper's GDPR-compliant approach:
- The consent forms are user-friendly, using simple and understandable language, with easy-to-use toggles for giving or withdrawing consent.
- The Guardian maintains detailed consent logs, keeping track of when and how consent was obtained.
- If a user withdraws consent, the company promptly reflects that choice in its systems.
Compliance Plus: Privacy by Design and Data Regulations
Navigating the data privacy landscape of regulations, including GDPR and CCPA, requires understanding their implications for personalized marketing.
Those regulations mandate transparency in data collection and use robust security measures and individual rights over personal data, requiring marketers to modify practices to ensure compliance.
That involves gaining informed consent, maintaining transparency, and respecting individual preferences. Those are not just legal requirements; they're crucial for building customer trust and reputation.
Compliance should be a start, not an endpoint. Businesses should adopt Privacy by Design, which is built on seven foundational principles:
- Mitigate privacy risks in advance. Anticipate and prevent privacy-invasive events before they occur. Microsoft exemplifies that principle by using robust security measures (encryption, threat detection technologies) to safeguard user data.
- Build systems that inherently protect privacy. Privacy should be an integral part of system design, not an add-on. Microsoft's commitment to privacy is ingrained in its operations, from the transparent privacy statement to the built-in privacy settings across its range of products and services.
- Put user privacy at the center. Keeping user privacy at the forefront means providing privacy-enhancing options. Microsoft's privacy dashboard allows users to view, manage, and delete their data.
- Balance functionality and privacy. The goal is to create a win-win scenario where both functionality and privacy coexist without tradeoffs. Microsoft strikes that balance by offering high-functionality products that are also designed to protect user privacy.
- Make privacy the standard setting. User privacy should be secured without any extra steps from the user. Microsoft supports that principle by providing users with privacy settings that give them control over their data. Users can determine whether their data is used for personalized ads or for improving Microsoft's products.
- Use transparent and clear practices. The system's functioning and data handling practices should be clear to all stakeholders. Microsoft's detailed privacy statement and proactive communication about its data practices embody this principle.
- Safeguard data at every step. Ensuring strong security measures at all stages of data processing. Again, Microsoft upholds that principle by securing users' data throughout their lifecycle.
For businesses, integrating the principles of Privacy by Design into their marketing strategies can facilitate a balance between effective marketing and user privacy. Again, it's not just about regulatory compliance, but about placing customer privacy at the core of business operations.
Learning From the Best: Case Studies in Privacy/Personalization Balance
Unilever and HubSpot offer compelling examples of how to judiciously harness user data to offer personalized experiences without undermining user privacy.
Their practices illustrate that respecting user privacy does not require compromises with personalization—that those two objectives can coexist and foster better customer relationships.
Case study 1: Unilever
Unilever, a global consumer goods company, balances personalized marketing with user privacy through a minimalist approach to data collection. By gathering just the essential data for personalization, Unilever reduces privacy risks while maintaining the ability to offer tailored content.
Transparency is another cornerstone of the company's strategy. Its privacy policy, which details data collection, use, and retention, fosters consumer trust and comfort.
Unilever emphasizes consent-based personalization, allowing users to select their level of personalized experience, respecting privacy and enhancing the reception of marketing messages.
Case study 2: HubSpot
HubSpot, a leading CRM, marketing, sales, and customer service platform, collects and analyzes data to improve user experiences. It's firmly committed to doing so within the bounds of privacy laws and regulations—anonymizing user data by removing any identifiable information, and providing users with clear settings for managing their data-sharing preferences.
The company gathers information about how customers use its products and services, analyzes data for content personalization, and tailors its communications based on a customer's preferences and history.
Summary of Main Ideas
The importance of prioritizing user-centric privacy in personalized marketing cannot be overstated. As businesses compete to deliver personalized experiences, privacy is a critical element that strengthens customer relationships. An approach that respects user privacy doesn't only ensure regulatory compliance; it also fosters trust, transparency, and brand loyalty.
The future of marketing will be increasingly centered on privacy. Because of evolving data regulations and increasing consumer consciousness about privacy, the focus will be on developing strategies that balance personalization with privacy.
That shift isn't a tradeoff between delivering tailored experiences and safeguarding privacy. Rather, it underscores that meaningful personalization can and should coexist with robust privacy protections.
More Resources on Customer Trust and Privacy
Consumer Trust and Privacy: The Marketer's Challenge
Balancing Consumer Trust with Privacy-Safe Targeting: Three Tactics
A Privacy-First World Won't Hurt Your Customer Relationships | Marketing Smarts Live Show