Google considers over 200 ranking factors when promoting webpages in SERPs, but almost all of them fall under one primary category: quality.
That's because Google is always trying to make search better for users. For a webpage to rank well, it must provide high-quality content and an elevated page experience. It should also come from a well-trusted, reputable website.
So how do site owners and digital marketers prove to Google that their content is not only relevant to users but also high in quality?
By improving content quality signals on their web pages. By focusing on those quality signals, digital marketers will have better SEO results across all of their landing pages.
How Does Google Define High-Quality Content?
Although having the right keywords is essential to showing Google that your landing pages satisfy search intent, Google's technology has gotten much more advanced over the years. It now looks for more than just keywords when deciding whether to rank your webpages.
Google also looks for high-quality signals such as the following:
- Original information, reporting, or research
- Comprehensive, substantial exploration of the topic
- Original insights and analysis
- Clear sourcing and expert authorship
- Accurate spelling, grammar, and error-free copy
Conversely, certain practices will cause Google to view your landing pages as low-quality. Some low-quality signals include:
- Automatically generated or scraped content
- Irrelevant, unnatural keyword usage
- Unoriginal, plagiarized content
- Excessive redirects, broken links, or hidden text
Google has always emphasized discovering unique and valuable content for users. Therefore, any digital marketer who wants to show up in search needs to aim for the same goal.
Five Content Quality Signals and How to Improve Them
1. Semantic richness: add subtopics, questions, and related topics to your landing page copy
Semantic SEO is the process of creating meaningful content that satisfies users' intent in addition to their specific query.
When semantic SEO is effectively implemented, Web content answers the users' questions as well as all of the questions they may have next.
The more semantically rich your content is, the more Google recognizes it as well-researched, informative, and original. To improve semantic richness on your page...
- Do competitive research. What type of content is already ranking on page one for the keywords you want to rank for? What types of words and phrases do those pages include in their content?
- Use a keyword tool. Identify related subtopics, synonyms, questions, and autocompletes related to your target keywords. Add them into your content to improve its semantic signals.
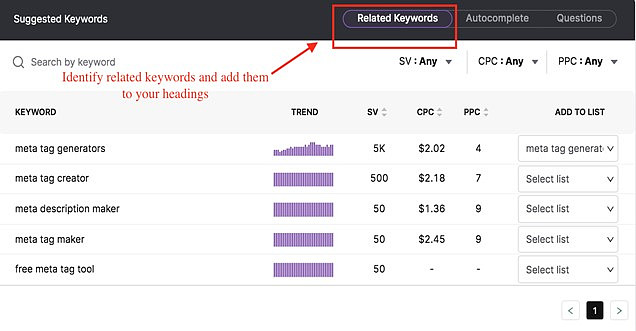
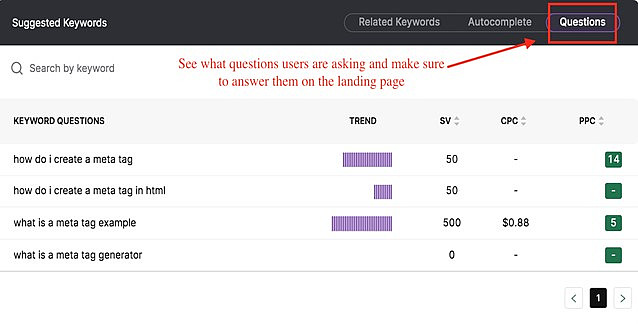
- Use content AI software. Software such as SEO Content Assistant can help you create more semantically rich content. Content AI tools use natural language processing to generate terms to add into your content to give it more ranking power.
2. Topical depth: increase the content length of your landing pages to match your competitors'
Technically, word count is not an official ranking factor for Google. So why does content length matter to SEO strategists?
Well, multiple studies have found a correlation between content length and a higher ranking. That's because in-depth content influences other elements that Google does take into consideration, such as...
- Backlinks: Longer content earns more backlinks. Backlinks are Google's #1 ranking factor, so the more backlinks, the better the ranking.
- Comprehensiveness: Long-form content shortens the amount of research the searcher has to perform independently. Web users prefer content that presents all necessary information in one place.
- Engagements: Long content tends toward better user engagements, such as longer page sessions, better scroll depth, and more clicks on submission forms, signups, and CTAs.
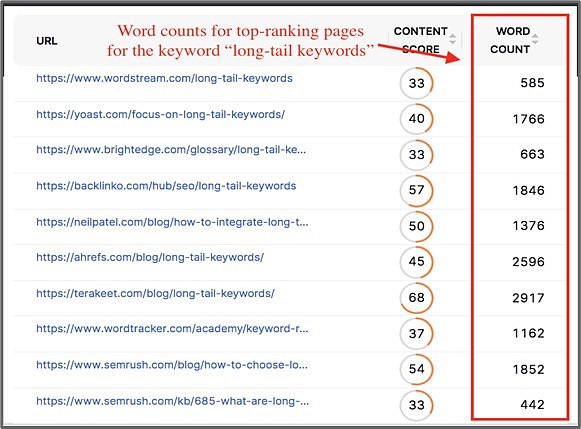
By increasing copy length on your landing pages, you're likely to increase other signals that Google associates with high-quality content. You can use SEO tools to identify the word count of pages that are already ranking in the top spots, then aim to create similarly in-depth content.
3. Interactive elements and rich media: ensure your content is backed by eye-catching, rich multimedia elements
Google cannot "see" videos or images, so it's essential to use descriptive image alt text so Google understands the relevance of your rich media to the user. Interactive elements on your page such as jump links and expandable content modules can also serve as high-quality signals to Google.
Some content marketers hesitate to use collapsible content modules, fearing that users may miss important information. But those types of interactive layouts can help you add content length to your landing pages without sacrificing user experience or making the page overwhelmingly text-heavy.
4. Page experience: troubleshoot Core Web Vitals in Google Search Console
In June 2021, Google rolled out its Page Experience update . The quality of a webpage's overall experience is now an official ranking factor.
Usability factors, such as mobile-friendliness, safe browsing, and intrusive interstitials, matter to ranking well in Google.
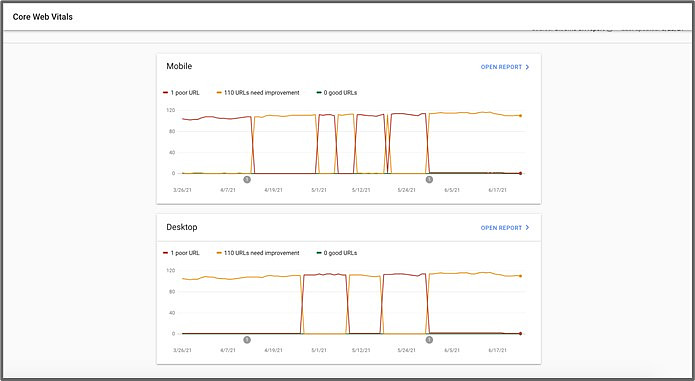
Thankfully, Google makes it simple to understand whether your webpages meet its quality standards. The Page Experience feature in Google Search Console allows you to identify and fix page experience issues.
Google's standards are called Core Web Vitals. They include...
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): The amount of time it takes for the largest image or text asset on the page to load
- First Input Delay (FID): The amount of time it takes your landing page to respond to the user's first click or engagement
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Whether your layout shifts while the user is on the page (nothing is more irritating to users than attempting to click on something and having the content shift beneath their cursor or finger)
5. Linking profile: link to expert sources and relevant content
The webpages you link to—and those that link to yours—tell Google a lot about the quality of the company you keep. To help Google consider your webpages high-quality, use external and internal links wisely.
Here are a few tips for linking:
- Use internal links to connect users to other relevant content on your website. Try to make the anchor text contextual so Google sees how your content relates to the content being linked to.
- Pursue only white-hat link building campaigns, and ensure any links you receive come from reputable websites via Google-compliant strategies.
- Include links to your integral pillar or category pages in your navigation menu. You can also use the navigation menu to direct users to your highest-converting pages.
To truly improve your website's performance, it is vital to understand how every component is communicating (or not communicating) high quality.
High-quality content is Google's guiding light; prioritizing it will always result in a much-needed edge over your competitors.
More Resources on Content Quality Signals
Eight Ways Your Content Marketing Might Be Sabotaging Your SEO
The Future of Link-Building: Linkless Mentions for SEO
How 'EAT' Helps Businesses Succeed on Google Search [Infographic]




