Every marketing strategy has a primary goal, whether that goal is to generate new leads, grow an email list, increase sales, or something else.
However, prospects rarely go straight from learning about your business to becoming a solid lead or actual customer. They need to engage with your brand multiple times before converting.
That means to achieve your primary goal, you have to focus on the smaller goals that move people through your funnel.
Those are called micro-conversions, and they are the focus of this article.
Read on to discover more about micro-conversions: what they are, why they matter, and how you can measure them.
What are micro-conversions?
To help you understand what a micro-conversion is, let's first take a look at the definition of a macro-conversion.
A macro-conversion is the primary goal of your website or landing page.
For an e-commerce retailer, a macro-conversion is the conversion of a visitor into a paying customer. For a software provider, however, a macro-conversion might be a solid lead, such as a request for a demo or quote.
Other examples of macro-conversions:
- A completed transaction
- A booking
- A free trial signup
- A completed lead generation form
Here is an example of a macro-conversion in action from Movavi, a video editing software provider.
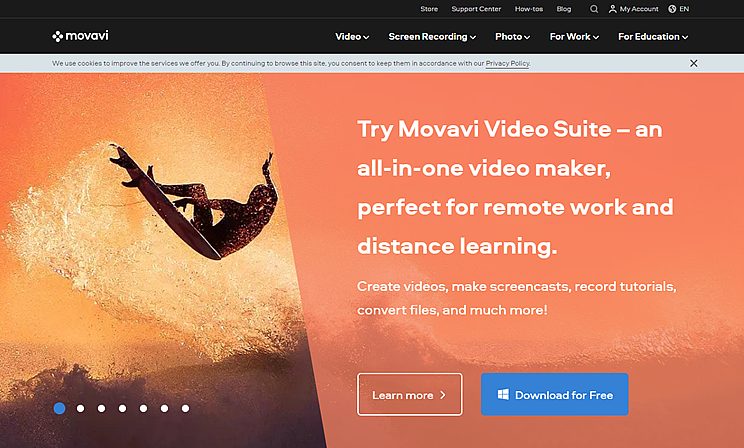
As you can see, the company's goal for the homepage is to get individual visitors or organizations to download its software for free, which creates leads that Movavi will later pitch the full product to.
Choosing the right macro-conversions depends on the industry you're in. Some examples:
- E-Commerce: Making a purchase
- Social networks: Creating an account
- Content websites: Signing up for an email newsletter
- SaaS companies: Requesting a demo
- Affiliate sites: Clicking a sponsored link
The common factor between these seemingly different goals is that each macro-conversion has an impact on the business's profits—either immediately, or very soon after.
A micro-conversion, on the other hand, is a smaller type of engagement that is a stepping stone toward a macro-conversion, such as signing up for a newsletter, watching a video, or downloading a whitepaper.
Basically, it's any activity that takes place on the customer's journey to a macro-conversion.
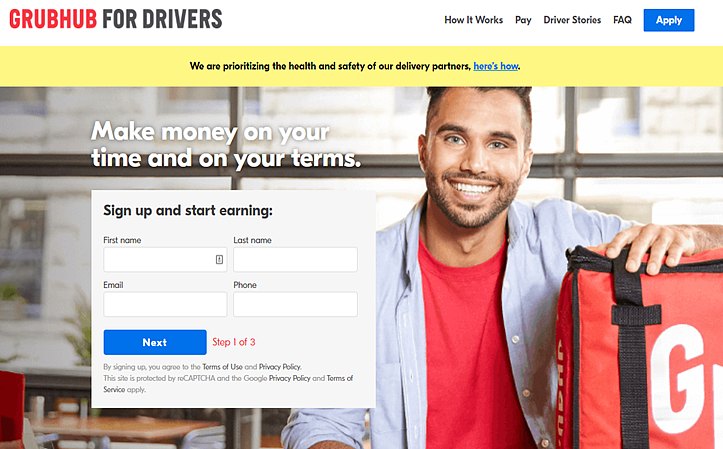
Here is an example of a micro-conversion in action from Grubhub when the company tries to get Grubhub drivers to sign up.
On this page, Grubhub is asking users for some personal information to get started. You may notice that this is step 1 of 3, which indicates a micro-conversion from filling out the form, but also from each click on "Next" to submit more data.
Other common micro-conversions:
- Sending a proposal
- Adding to a wishlist
- Liking or upvoting
- Filling out a contact form
- Data from digital drip campaigns
- Subscribing to a blog
- Scrolling down a page
- Adding products to a shopping cart
- Sending a Facebook or LinkedIn message
- Executing a product search
- Navigating through a catalog
- Clicking on a search result
- Browsing X number of products
- Commenting on a blog or social post
- Viewing X number of pages on your website
- Creating an online account
- Liking or following a brand on social media
- Visiting specific pages, e.g., pricing page, features page, etc.
- Sharing a blog or social post on social media
The list goes on!
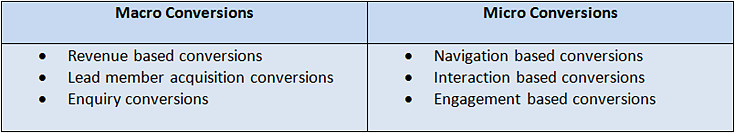
The following image summarizes the differences between micro- and macro-conversions:
Why do micro-conversions matter?
Now that you know what micro-conversions are, it's time to take a look at why they are so important, and how monitoring them can have a massive impact on your business. Macro-conversions are arguably more important because they correlate directly with revenue, but they're not the only meaningful events taking place on your site.
Customers typically complete multiple micro-conversions before they reach a point where they are comfortable making a purchase. That's why, if you focus only on your primary goal, you'll miss out on many opportunities. Micro-conversions nudge your audience forward in your funnel to achieve your primary goal, which is the macro-conversion.
Just because visitors don't convert into actual customers the first time they land on your website doesn't mean the traffic is worthless. It's a part of the process; it can't be eliminated, so businesses shouldn't try to eliminate it. Instead, they should figure out the value their audience is looking for.
Micro-conversions come with a lot of benefits that can improve your overall conversion rate—and, therefore, your bottom line.
How can tracking micro-conversations benefit you?
1. Gauge user interest
Smaller types of engagement are important stepping stones used by people prior to making macro-conversions, and they can be useful indicators of a potential customer's interest in your product or service.
For example, if someone reads a couple of articles on your blog before signing up for your blog's weekly newsletter, that person is showing an interest, which could lead to a sale in the future.
2. Understand buyer behavior
Micro-conversions help you paint a clearer picture of your visitors and their activities on your website or landing page.
When you understand why people behave the way they do, it's a lot easier to develop targeted campaigns that help to improve your conversions.
For example, if someone executes a product search on your site, adds items to the shopping cart, and then abandons the cart, it could be an indication that your checkout page needs improvement.
3. Find areas for conversion optimization
By monitoring micro-conversions, you will collect lots of information pertaining to your website visitors.
That, in turn, gives you the ability to spot weak links in your funnel and diagnose areas of your website or landing page that need improvement for you to achieve higher conversion rates.
For instance, an online company might add a CTA button to its store homepage. Though that may not instantly boost sales, it will definitely become an indicator for your customers that there is an easy way to get in touch with you—which is your first step on the way to increasing your conversions.
Monitoring micro-conversions is especially useful for low-traffic websites that tend to be vulnerable to the effects of poor UX. When visitor numbers are low and you get only a handful of macro-conversions each day, you can make the most of each and every person that browses your site by analyzing micro-conversion statistics.
You'll get a lot more data than you would from looking at macro-conversions alone.
4. Track users across channels
Tracking micro-conversions also allows you to collect user information across various channels.
That will help you determine specific things that can inform your marketing strategies, such as which traffic sources lead to more conversions, the social channels preferred by visitors for sharing your content, and so on.
5. Measure engagement
Another reason to monitor your micro-conversions is that it helps you see just how effective your webpages are at engaging visitors.
For instance, you can look at how many people view more than a couple of articles on your blog to see how appealing your content is to your visitors, as well as how easy your site is to navigate, how effective the "related content recommendations" are, and so on.
6. Nurture leads
Micro-conversions allow you to nurture your ideal visitors. When visitors fill out a contact form on your site, that micro-conversion provides you with the perfect "foot-in-the-door" moment to start nurturing leads.
One example can be found on the free course page of my site, OneHourProfessor.com:
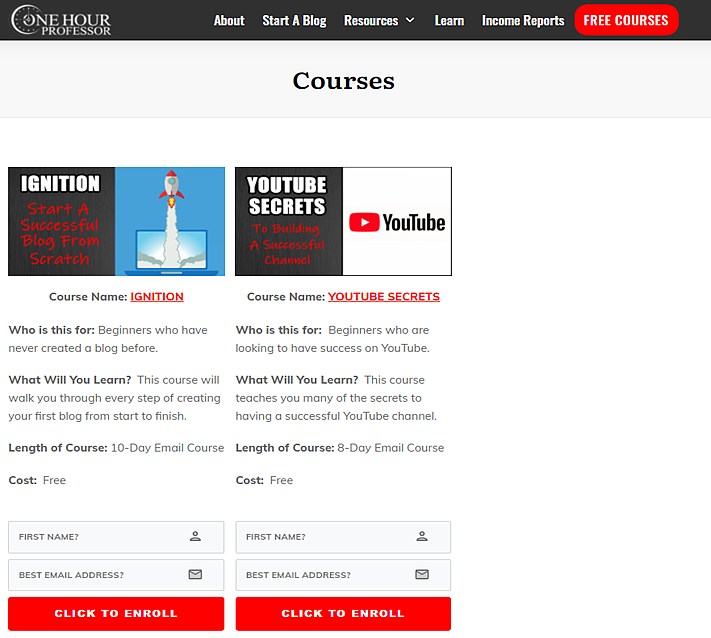
The objective of the page is to get visitors to sign up for a free course. While the visitors go through the funnel, they learn about various ways of making money online, such as starting a blog, building and selling online courses, using affiliate marketing, and more.
Another example of how you can use micro-conversions to nurture leads is by offering first-time visitors a discount in exchange for joining your email list.
That serves a dual purpose. First, the discount itself may lead to a transaction. Second, the email allows you to continue the conversation with the visitor, thereby improving the chances of getting a macro-conversion.
7. Understand the customer journey
Micro-conversions also help you to better understand the customer journey. This is particularly important for websites where the sales cycle is longer and more complex, requiring lots of information and plenty of discussions before completion.
For those companies, it's not enough to simply sell; they also need to be able to provide their visitors (both current and potential customers) with information on their products and services, how they work, the industry in general, etc.
In such cases, tracking micro-conversions helps to outline the complete customer journey.
How do popular brands track micro-conversions?
Before we look at how to track micro-conversions, here are a few examples of how some big brands are using micro-conversions to help them achieve their primary goals.
AppSumo: Capturing an Email
As a micro-conversion, capturing an email is one of the most important for most businesses. After all, email has the highest ROI of any marketing channel.
But as any marketer will tell you, it takes a lot to convince someone to opt in to a brand's email communication.
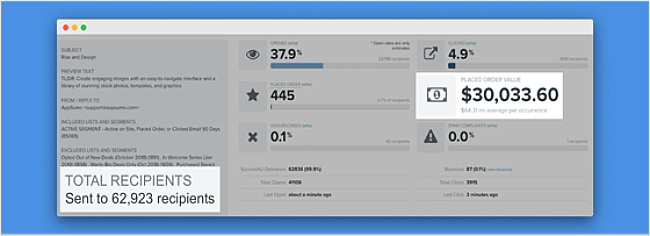
AppSumo is an example of a brand that takes advantage of email micro-conversions in a powerful way. It sends weekly emails to over 60,000 recipients, which results in an average of $30,000 revenue per weekly email campaign.
HubSpot: Creating an Online Account
Whenever a potential customer takes the time to create an account on HubSpot, it's a micro-conversion for the SaaS company. Although the action might not directly lead to a sale, it certainly improves the chances of the visitor's returning to make a purchase at a different time.
So, although the user might consider the action insignificant, it ultimately makes a huge impact on the company's likelihood of getting a macro-conversion.
Autofill features on browsers can further simplify the process of signing up for a new account—visitors can have an account set up with just a couple of clicks.
How do you track micro-conversions?
Tracking micro-conversions can be done through behavior analytics platforms that show you exactly how users make use of your website and landing pages, thereby giving you deeper and more powerful insights into what you can and should change, as well as when to change it.
Alternatively, you can use Google Analytics, simple and free Web analytics software. Google Analytics allows you to track micro-conversions in the same way you would macro-conversions.
In Universal Analytics, or the new Google Analytics 4, you can log conversions as either GA "Goals" or "Events."
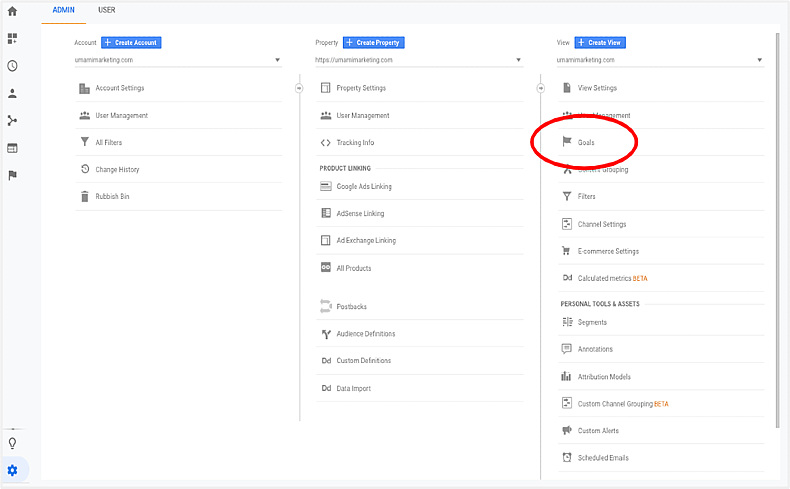
Step 1: Click "Goals" under the "Admin" section of your GA account.
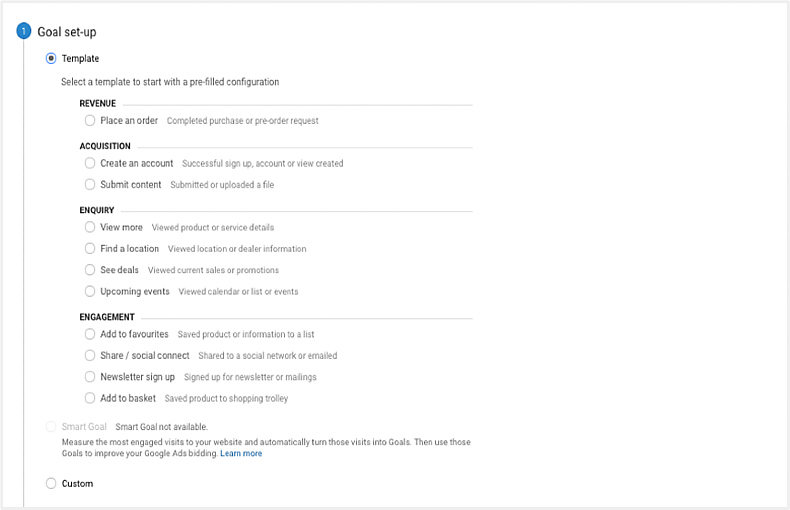
Step 2: Click "+ New Goal" to set up your micro-conversion goal. You can use one of the templates it provides.
Step 3: To complete the setup, name your goal and specify how you'll track it.
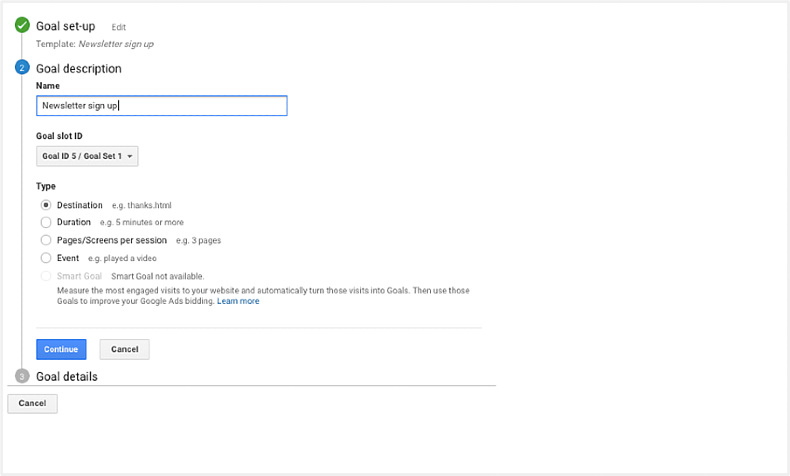
When you have completed the goal setup, you'll be able to track that goal's conversions through your Analytics account in the overview section (Conversions > Goals > Overview), where you'd normally track your macro-conversion goals.
Which micro-conversions should you track?
Every customer goes on a journey before deciding whether to buy your product or service. There are so many practical applications for micro-conversions in B2B and other industries that it's worth thinking about which ones have the most impact on your business, and track those.
If you fail to identify and measure micro-conversions and take them into account as part of your SEO strategy, you'll miss out on massive opportunities to grow your business.
As evidenced by the examples in this article, even tiny improvements compound and produce huge payoffs. So, use this information to help you track and measure micro-conversions that are most important in your ideal customer's journey so you can improve results and boost your bottom line.
More Resources on Micro-Conversions
One Tip to Improve On-Page SEO: Use More Mini-Infographics (A Guide)
How the AdWords Conversion Reporting Updates Enable Better Tracking of Macro- and Micro-Conversions




