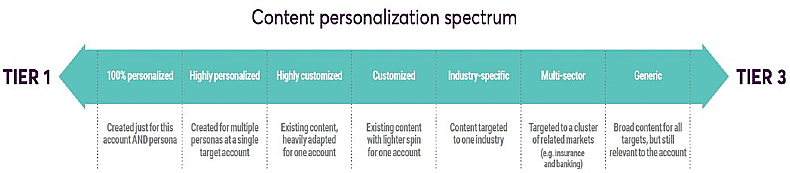
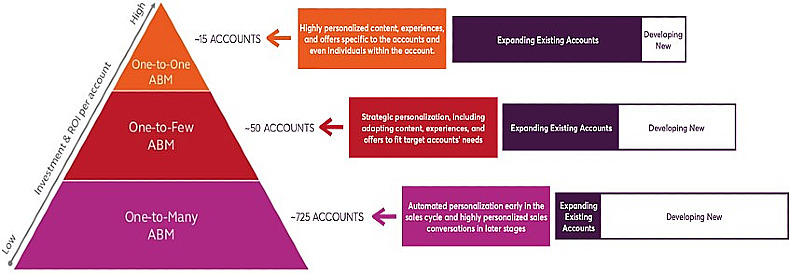
The popularity of account-based marketing in B2B is increasing—for good reason. It's highly effective because it relies on communication that targets carefully and narrowly defined audience groups rather than a scattershot approach.
ABM encompasses long-term activities and focuses heavily on adjusting the content to the audience—not only for selected accounts but also for selected people within a particular company. As a result, it increases pipeline velocity and helps to expand business with current accounts.
What Account-Based Marketing Is

AMB ensures full synchronization of Marketing and Sales activities right from the start. The cooperation of those two departments begins at the stage of building and prioritizing a list of targeted accounts, or customers with whom the company plans to expand business. The process is called the prequalification of leads.
In traditional digital marketing, qualification usually takes place after generating a lead, but in the ABM approach, marketers select interesting leads before even obtaining their contact details. ABM is like hunting with a spear instead of a net:

Account-based marketing can take the form of a one-off activity, such as account-driven activation (think a grand gesture as an act of marketing), or it can serve as a long-term account-driven business strategy. The latter approach takes longer to develop, but it brings results more consistently and influences overall deal velocity. (This GENESYS case study is a good example.)
Core operational goals of ABM strategy:
- Demand generation: stimulating business demand, influencing potential accounts, and generating better-qualified opportunities for the future
- Pipeline velocity: shortening the customer journey through the funnel by encouraging the purchase decision with more convincing, targeted marketing messages
- Account expansion: increasing revenue from one account and limiting churn
Account-Based Marketing Challenges and Analytics
When using an ABM strategy, companies should understand that the success factor is demand generation—influence over time—rather than one-off lead generation activity.
Lead generation often means obtaining consent to send marketing and sales communication, even though those giving consent often are not ready for contact, nor would even consider having a sales meeting, because of the positions they hold (think C-level management in the largest companies).
That approach triggers radical changes in the ways you measure the results of campaigns implemented in the ABM framework.
Instead of counting "leads," marketers should measure how many times individual people representing hand-picked accounts had contact with their company's brand and communication materials.
The main challenge of ABM performance analytics lies in evaluation of the power of marketing communication and validation of individual tactics applied. It is difficult to identify "last clicks," a technique used in e-commerce or SaaS. Individual registrations for events or e-book downloads might also not be as important in a success attribution model. B2Bs—specifically, the enterprise segment—tend to have different dynamics and structure in the purchasing process:
ABM performance analytics should focus on the involvement of the account (and its employees) in the communication you conduct. Distinguish between so-called passive engagement (the account saw our ad!) and active engagement (the account clicked, downloaded, and participated).
Active engagement over time may qualify the client as an opportunity that Sales can then validate—an important change, because in ABM, Sales validates opportunities rather than incoming leads.
As activities unfold, data collected over a longer period should allow marketers to confirm whether their strategy increases the revenue from a single account and whether it shortens the time necessary to win it. That requires close involvement of the sales team and the tracking of CRM metrics (date lead was added to CRM, date of opportunity, previous and expected opportunity value, etc.).