It's no secret that SEO is changing fast. So fast, in fact, that many small business owners have trouble keeping tabs on what is (and isn't) important in the world of SEO.
Back in the early days, things were simpler. SEO was all about title tags, keywords, and backlinks. Today, a successful SEO campaign needs to take into consideration branding, user experience, semantic search, and much more.
Not to mention that Google continues to move the goalposts on a daily basis. In fact, Google has confirmed that on average it makes two change to the algorithm every day.
Fortunately, a team of SEO professionals led by Brian Dean came together to shed some light on what's important in the world of SEO in 2016. The team recently analyzed 1 million Google search results to determine which ranking factors correlate with first-page Google rankings. (Read the full report.)
Here are the six most important takeaways from the study.
1. In SEO, content is king
The study found that content with two key characteristics significantly outperformed content without these characteristics.
Those two characteristics were content length and topical authority.
The research team discovered that long-form content was significantly more likely than short content to wind up at the top of Google's first page:
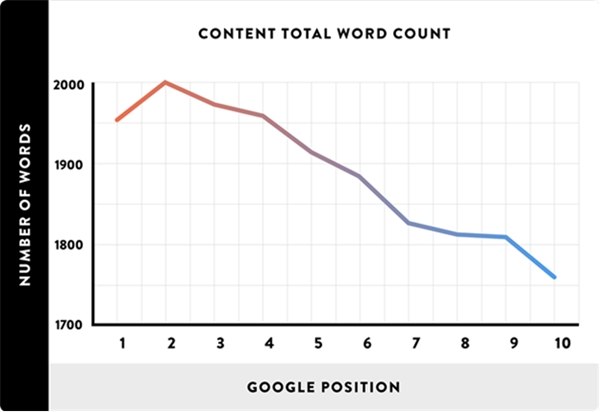
Interestingly, they discovered that the average piece of content on Google's first page contained 1,890 words, a number that flies in the face of many content marketers' practice of writing short blog posts. Yet, those findings are consistent with other industry studies that have found a correlation between content length, shares, and Google rankings.
The report also states that highly valuable, in-depth content tended to rank above content that only skimmed the surface of a topic. Using a software product called MarketMuse, they analyzed the articles in their data set and scored them for comprehensiveness.
Articles with a higher authority score significantly outperformed content with a low score:
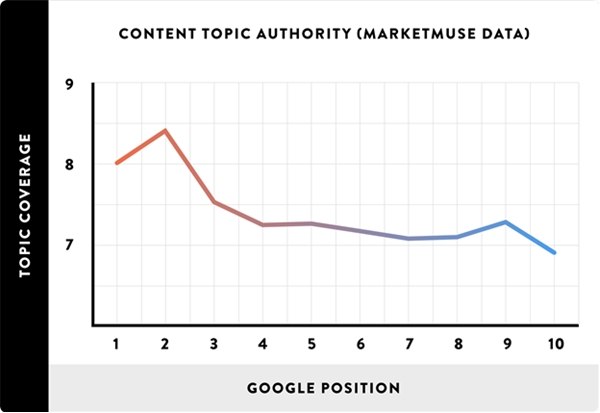
As Google comes to better understand content's underlying topic (thanks to Semantic Search), Google may be gaining insight into content's ability to cover a topic in depth.
Key insight: Writing long-form content that covers a single topic in depth may be important for Google rankings in 2016.
2. Backlinks are here to stay
Even though backlinks formed the foundation of Google's original PageRank algorithm, spammers and "black hat SEOs" were able to successfully game the search engine giant's algo with phony links.
So there's been a lot of talk over the past few years about Google's move away from backlinks.
However, according to the study, backlinks remain an integral part of how Google views a page's authority. Of all the factors that the study authors investigated, the number of different links pointing to your page from unique domains was found to be the most important.
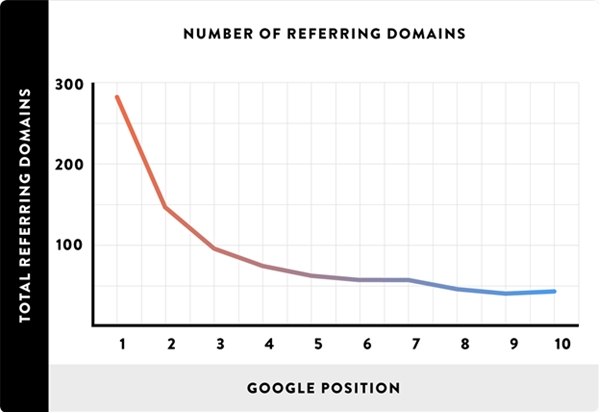
Does this mean that you should head over to Fiverr and order 5,000 article directory backlinks? Of course not. However, it does suggest that moving away from link-building entirely may be a mistake. Google employees have even gone on the record to say that there's nothing inherently wrong with link-building—assuming the links are built using legitimate tactics.
Key insight: Building legitimate, white-hat backlinks from different sites may have a significant impact on your Google rankings.
3. Don't believe the Schema hype
When Google joined forces with Yahoo and Bing to create a standardized code for structured data—resulting in Schema.org—many digital marketers thought it would usher in a new era of search engine optimization. Unlike the old days, when you told Google about your page by stuffing keywords in your content, you could now use Schema instead. And, in fact, Google has suggested that Schema may become a ranking signal in the near future.
Though Schema may be helpful in certain circumstances, it doesn't appear to have an impact on SEO. The report states, "Despite the buzz around Schema, our data shows that use of Schema markup doesn't correlate with higher rankings."
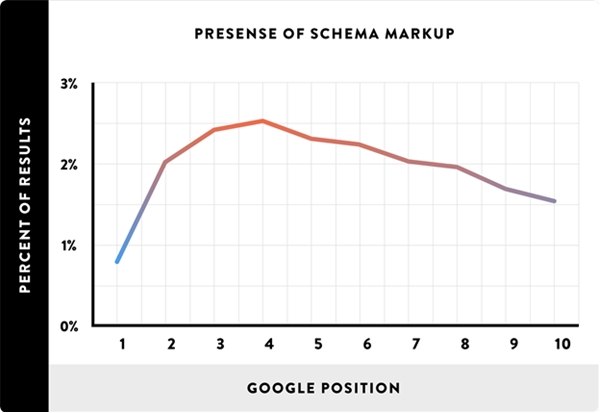
One important caveat is that structured data isn't always implemented correctly. As one of the authors states in a blog comment, "another consideration we had is that so many website implement schema poorly (for example) that they could even be hurting themselves a little bit. Schema is also very dependent on the type of content on your site. B2B sites, for example, don't have as much opportunity in general to use it wisely."
The study didn't distinguish between properly and improperly implemented structured data. Therefore, it may be that Schema, when used correctly, helps with rankings.
Key insight: Simply adding Schema.org markup to your pages is unlikely to make a significant difference in your search engine rankings.
4. There's no need to keyword-stuff your title tags anymore
As I noted, Semantic Search allows Google to get a true understanding of your page's topic (no keyword stuffing required). Interestingly, the study found that including your target keyword in your title tag does help with rankings; however, the correlation was significantly lower than the experts involved with the study expected.
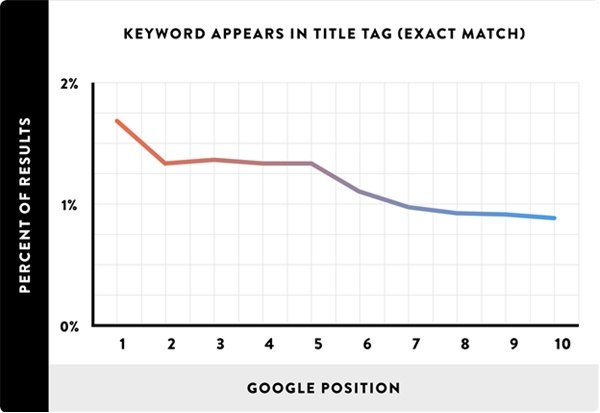
For those of you that prefer to "write for people, not search engines," this finding may come as a sigh of relief. Although keyword optimization is still important, this data suggests that Google may not need to see your exact keyword in your title for you to rank for that keyword.
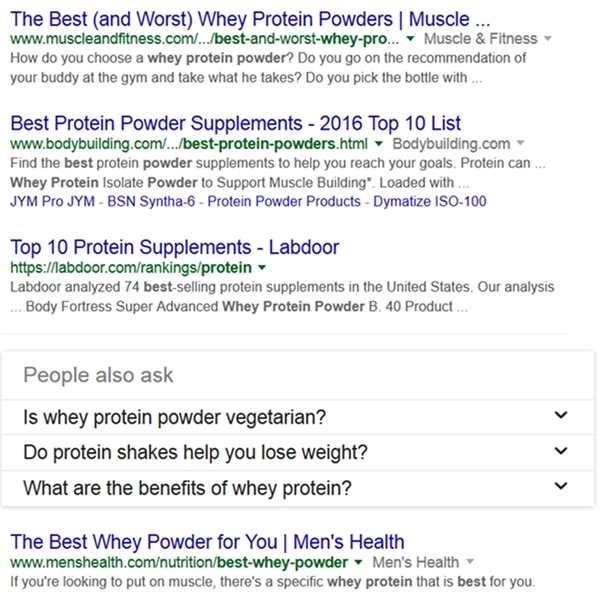
For example, if you search in Google for "best whey protein powder," only one of the four top results contains the words in "best whey protein powder."
Key insight: Don't stress about including your target keyword in your title tag. Instead, write a title that encapsulates your page's content and attracts clicks.
5. Don't slip on site speed
When Google first announced that it was going to use pageload speed as a ranking signal, it sent the SEO world into a frizzy.
It's not often that Google comes right out and says, "Do this and expect higher rankings." And when it's something as easy to implement as site speed? It's a no-brainer.
According to this new study, site speed shouldn't be something left on your company's back burner. Faster sites tend to rank above slower sites:
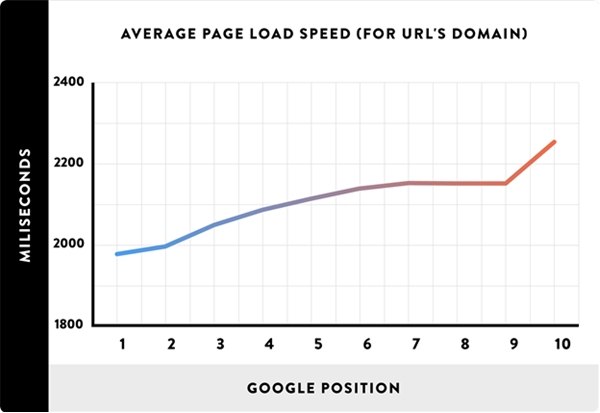
Despite the proven importance of website loading speed, I still come across sites that load slower than a snail stuck in superglue. And the crazy thing is that—in the case of WordPress-powered websites—boosting your site speed is an absolute walk in the park.
Even if you don't run your site on WordPress, there are still some simple steps you can take to get your site up to speed (literally). Here are a few of the most impactful steps you can take:
- If your site does run on WordPress, install and activate the WP Smush and WP Rocket plugins. Those two plugins alone can halve your loading time.
- Install and use a CDN, such as MaxCDN. Doing so can get messy if you don't know what you're doing, so get a developer to help you.
- Speaking of developers, I'd hire one that specializes in site speed. You'd be surprised what a skilled coder can do with two hours of speed optimization. Ask around for a recommendation or use a site such as Upwork to find a seasoned pro.
Key insight: Site speed matters. Check your site's speed using Google's PageSpeed Insights and then, to measure their impact, implement the steps I've outlined.
6. Reduce your bounce rate
Many of the factors that I've mentioned so far (such as backlinks and title tag optimization) are old-school SEO mainstays. However, there are a slew of new ranking signals that Google may be using today.
One set of these new ranking factors is known as "user experience signals," which include things like bounce rate, time on site, and click-through rate.
The study found that one of these user experience signals—bounce rate—correlated with Google rankings:
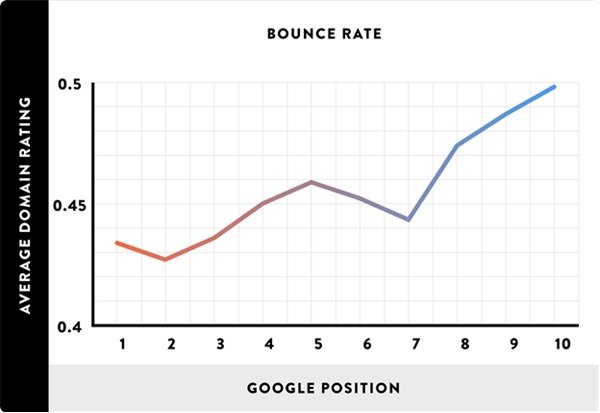
Specifically, it discovered that sites with lower bounce rates tended to rank above sites with higher bounce rates.
Although that's an interesting finding, it's not clear whether bounce rate, per se, has a direct effect on rankings. Dean was quick to point out that this finding may be a classic case of correlation not equaling causation, because "lower bounce rate is a byproduct of high-quality content, which Google does measure."
In other words, sites with great content may have a lower bounce rate simply because people enjoy reading their articles.
* * *
SEO is an ever-changing landscape, but keeping these six factors tips in mind can ensure that you're focusing on the right SEO strategies in 2016.




